 |
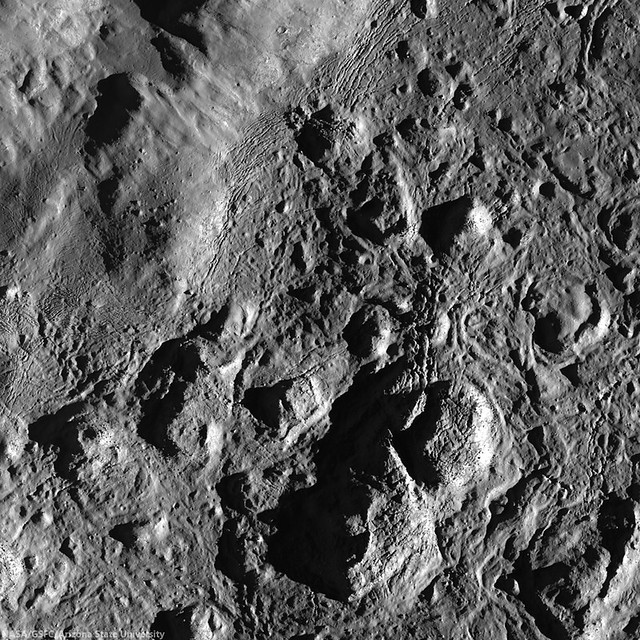
| Solidified impact melt on the floor of farside crater Jackson, a silent testament to a violent impact event. LROC Featured Image, released January 9, 2014. 700 meter field of view from LROC NAC M1139975629RE, LRO orbit 20,065, November 24, 2013; native resolution 1.39 meters [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University]. |
Raquel Nuno
LROC News System
The beautiful, jagged complex patterns seen on the floor of Jackson crater were formed when an asteroid slammed into the Moon at ~20 km/s (44,740 mph). This violent event likely occurred less than 500 million years ago, young by lunar standards.
Jackson crater is located on the farside of the Moon centered at 21.788°N, 164.92°W. This spectacular image was taken when the Sun was low on the horizon, causing dramatic lighting to accentuate the small topographical differences in the floor of Jackson crater. There are fantastic examples inside Jackson crater of the variety of morphologies that impact melt can produce.
During an impact event, tremendous amounts of kinetic energy are transmitted from the bolide (comet or asteroid) into the target rock. Shock waves cause the rock to melt almost instantaneously! Most of this molten rock accumulates within the crater, but some can be ejected outside, and some flows back into the crater, in many cases freezing on the way down forming spectacular cascades. As the crater is forming, material from the crater walls slump into the still hot impact melt, creating a lumpy mixture of intact target rock and shocked target rock. The slumping of material causes the melt to slosh around, forming ripples and waves which then harden as the impact melt cools. Solidifying and cooling causes shrinkage and cracking in the rock.
All of these impact features can be seen in today's Featured Image: impact melt ponds on terraced crater walls, impact melt channels, impact breccias, pressure ridges, and fractured melt sheets.
Can you find the different impact melt morphologies in the the full resolution NAC, HERE?
Related LROC Posts:
LROC News System
The beautiful, jagged complex patterns seen on the floor of Jackson crater were formed when an asteroid slammed into the Moon at ~20 km/s (44,740 mph). This violent event likely occurred less than 500 million years ago, young by lunar standards.
Jackson crater is located on the farside of the Moon centered at 21.788°N, 164.92°W. This spectacular image was taken when the Sun was low on the horizon, causing dramatic lighting to accentuate the small topographical differences in the floor of Jackson crater. There are fantastic examples inside Jackson crater of the variety of morphologies that impact melt can produce.
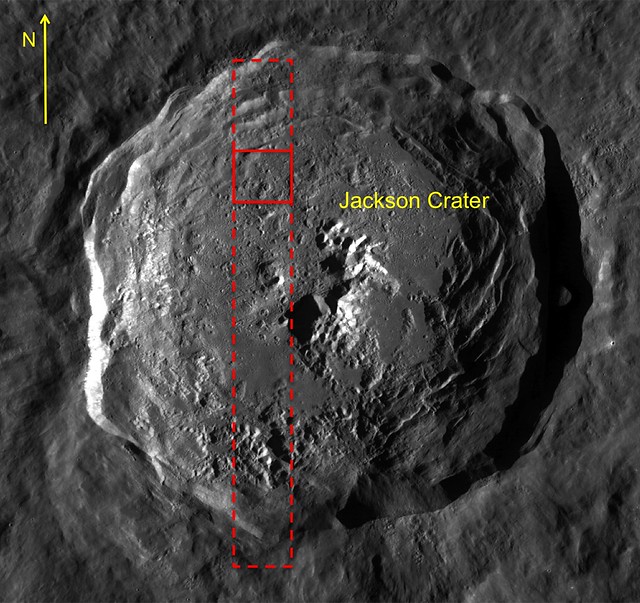 |
| LROC Wide Angle Camera (WAC) context image for Featured Image released January 9, 2014. Dashed rectangle outlines LROC NAC observation M1139975629RE [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University]. |
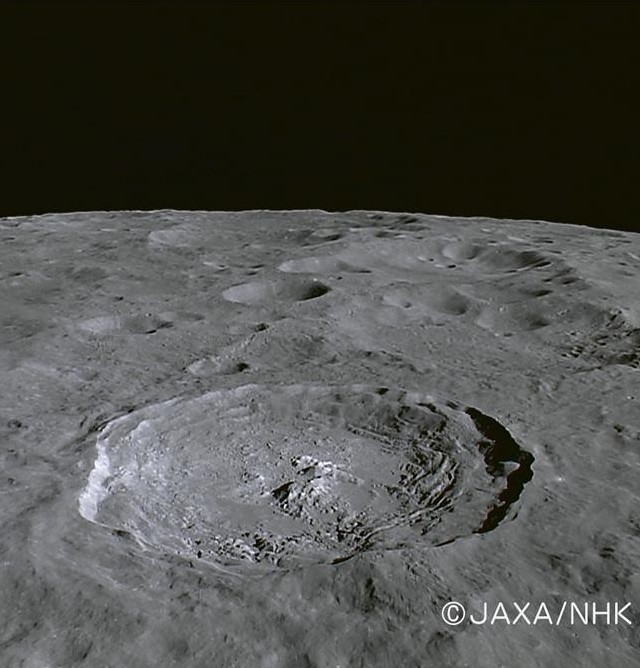 |
| Farside Copernican age landmark crater Jackson viewed through NHK's HDTV camera aboard Japan's lunar orbiter SELENE-1 (Kaguya) in late 2007 - enlarged 16:9 aspect HERE [JAXA/NHK/SELENE]. |
Can you find the different impact melt morphologies in the the full resolution NAC, HERE?
Related LROC Posts:
X marks the spot on the floor of Stevinus (January 7, 2014)
Fractured melt rock on Jackson's terraced wall (October 22, 2013)
Fractured melt rock on Jackson's terraced wall (October 22, 2013)
The peculiar domes of Stevinus (April 23, 2013)
Melt fractures in Jackson crater (January 20, 2012)


No comments:
Post a Comment